The following section outlines the most common Enterprise LLM integration pattern for customer who wish to use their self-managed Azure OpenAI endpoints and models.
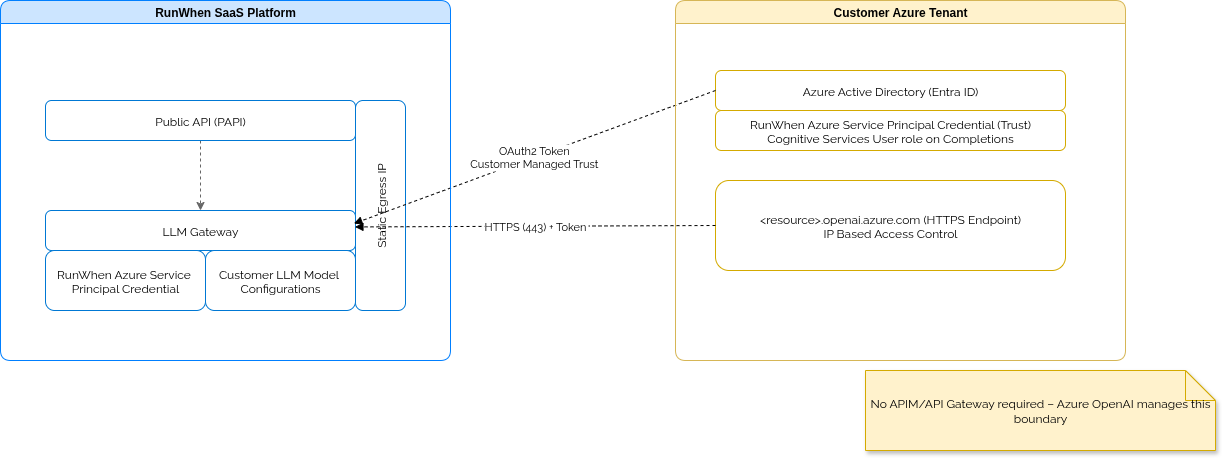
Customer Trusts RunWhen-Owned SP
-
SP Creation by RunWhen
-
RunWhen owns and manages a Service Principal (
appId,objectId) in its own Azure AD tenant. -
This SP identity never leaves RunWhen control.
-
-
Customer Establishes Trust
-
The customer grants this SP access by assigning it a scoped role (e.g.,
Cognitive Services OpenAI User) on their Azure OpenAI resource. -
This is effectively cross-tenant trust: the customer’s Azure subscription trusts a foreign SP identity from RunWhen’s tenant. The customer does not need to store any SP secrets inside of RunWhen.
-
-
Authentication & API Access
-
RunWhen uses its own SP to authenticate against Azure AD (customer’s tenant) when requesting access to the customer’s Azure OpenAI endpoint.
-
Azure AD enforces the RBAC role binding before issuing a token.
-
RunWhen then calls the customer’s Azure OpenAI endpoint directly with this token.
-
-
Network Security
-
Customer enforces IP allowlisting to ensure only RunWhen’s static egress IPs can reach the endpoint.
-
Optionally, the customer can also configure Private Endpoints/VNet integration if they want to force private access paths.
-
Azure OpenAI Endpoint Publication
-
Per-Resource Endpoints:
Each Azure OpenAI Cognitive Service deployment publishes its own fully qualified domain name (FQDN), such as:https://<resource-name>.openai.azure.com/ -
Regional Hosting:
These endpoints are region-specific (e.g.,eastus,canadacentral) and are managed entirely by Microsoft within the customer’s chosen region. -
Transport Security:
Endpoints are TLS/HTTPS secured, and Microsoft manages certificate rotation and availability. -
Direct Access:
Because the endpoint is customer-owned (tied to their Azure resource), all data remains within their Azure tenancy. RunWhen simply consumes the API using the SP-authenticated request.
Network Security and IP Whitelisting
-
RunWhen Source IP:
Customers can restrict access to their Azure OpenAI resource by whitelisting the RunWhen platform’s static egress IP(s). -
Resource-Level Network Controls:
Azure Cognitive Services resources support network access restrictions:-
Public access disabled (only selected IPs allowed).
-
Virtual Network (VNet) integration if customer enforces private endpoints.
-
-
Result: Only requests originating from RunWhen’s trusted IPs, authenticated with the customer’s SP, will be permitted.
No Additional API Management Layers Required
-
Why APIM/API Gateways Aren’t Needed:
-
Azure OpenAI service itself acts as the secured API boundary.
-
Identity validation (via Azure AD) and network restrictions (via IP allowlists/private endpoints) are natively managed.
-
This removes the operational overhead of deploying API Management (APIM), WAF, or custom gateways as intermediaries.
-
-
Simplified Data Flow:
RunWhen Platform ──(SP Credential + OAuth2 Token)──▶ Customer’s Azure OpenAI Endpoint
Customer Benefits
-
Full Control: Customers retain ownership of the Azure OpenAI resource, policies, and access control.
-
Minimal Trust Surface: The only trust granted to RunWhen is the scoped SP credential, limited by role and network allowlist.
-
Compliance-Friendly: All data processing remains within the customer’s Azure environment; RunWhen only initiates API calls.
-
Operational Efficiency: No need to manage redundant gateways or API layers, since Microsoft ensures endpoint security, availability, and scaling.
